The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate, and moderate-protein diet that has been proved to be an effective treatment among patients with epileptic conditions, such as glucose transporter 1 deficiency, pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency, tuberous sclerosis complex, Rett syndrome, Dravet syndrome, and specific mitochondrial disorders (1, 2).
The keto diet is also associated with successful weight loss and improving insulin resistance, which is why it can be particularly beneficial for patients who are obese or have type 2 diabetes (3).
There are also many major benefits of the ketogenic diet, such as improving cardiovascular health and brain function. Additionally, it has therapeutic effects for several other chronic conditions.
Something to keep in mind is that there is a huge difference between ketosis and ketoacidosis.
Ketosis is a natural metabolic state, whereas ketoacidosis, also known as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), is a dangerous condition in people with diabetes.
Nonetheless, the keto diet could also have some adverse effects, although most of them are temporary and are easily treated.
Below you’ll find a list of the possible negative side effects of the ketogenic diet.
They mostly occur in the beginning, during the first 1-3 weeks of your diet, and will usually go away on their own once you are fat-adapted.
Quick Summary: Most of the ketosis side effects and symptoms are only temporary and NOT everyone will get these. In fact, a lot of people thrive on keto without experiencing any negative effects at all. However, if you plan to start a ketogenic diet, always consult with your doctor first.
What Are The Most Common Possible Side Effects?

#1. Keto Flu
One of the most frequent adverse effects of the keto diet is the “low-carb flu” or “keto flu”, sometimes known as the induction flu.
Symptoms usually include headache, weakness, brain fog, increased hunger, and fatigue.
This happens because your body runs on glucose for energy, which it derives from carbohydrates.
By reducing your carbohydrate intake on a ketogenic diet, your body starts burning fat, and switches to a metabolic state known as ketosis (4).
However, your body needs a few days to adjust to this new metabolic state. During this period, you could experience flu-like symptoms.
These symptoms can last between 2-3 days or up to 2-3 weeks for some people, which is the time your body needs to adapt to being constantly in ketosis.
Not everyone will experience the keto flu, though. It depends on your body, on how carb heavy your previous diet was, and also on whether you’re mindful of your electrolyte and water consumption.
In order to combat the keto flu, you need to make sure you’re staying hydrated, and also to keep an eye on your electrolytes.
In fact, if you manage your electrolytes correctly from the beginning, you might not even experience the keto flu at all.
Something that could help you is a glass of water and half a teaspoon of salt, which can help improve the symptoms in less than 30 minutes. Taking electrolyte supplements or drinking bone broth can also help.
Bone broth takes hours to cook properly. If you don’t have time to make it, you can try these bone broth liquid and powder products.

#2. Keto Bad Breath
Another common side-effect of the keto diet is bad breath or acetone breath.
Acetone is one of the ketone bodies. They are formed during ketosis and the smell resembles fruit, or nail polish remover (5).
During the adaptation phase, your ketone levels rise, but your body isn’t yet prepared to use them effectively. This is why it gets rid of them via your breath or your urine (6).
So if your breath smells fruity, this is actually good news! You’re in ketosis now!
This adverse effect is also temporary and usually, after 1 or 2 weeks, it goes away on its own.
Nevertheless, there are some strategies to help with the so-called keto acetone breath:
- Stay hydrated
- Keep excellent oral hygiene. Do not forget to brush twice a day and also floss often.
- Use a breath freshener or sugar-free gums. Mint or spearmint chewing gums or mouth sprays can mask the bad breath

#3. Digestive Problems
Common issues with the keto diet involve digestive problems, such as constipation or diarrhea, even among children (7).
Lack of fiber on the ketogenic diet is likely to cause constipation, especially in the beginning (8).
Although constipation can happen to some people, it is easily treatable. Some simple tricks to avoid or treat constipation include:
- Staying hydrated, while at the same time increasing your and electrolyte intake
- Eating more non-starchy and fiber-rich green vegetables.
- If constipation continues, you could consider magnesium supplements or probiotics (9).
Some people also experience diarrhea, and that is usually the case when they increase fat consumption together with restricting carbohydrates.
Your body needs time adjusting to this new ratio of nutrients, so just be patient and do not reduce the fat intake.
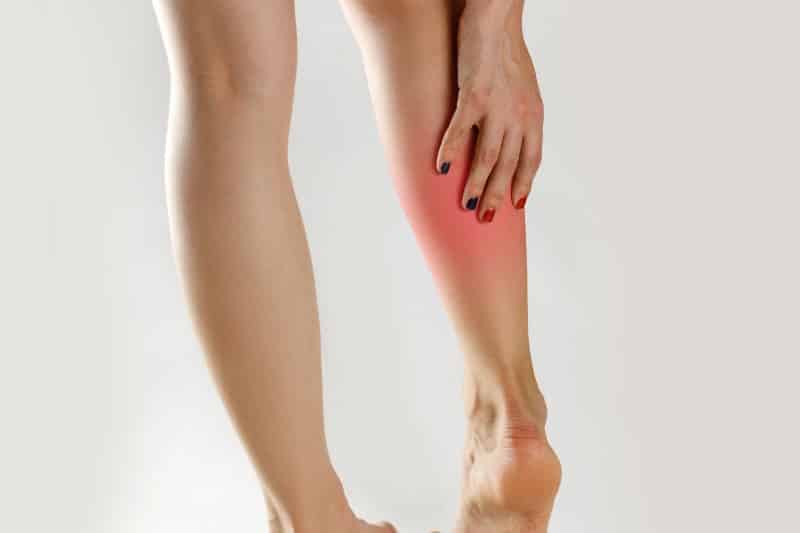
#4. Leg Muscle Cramps
While on the keto diet, it is not uncommon for people to experience muscle cramps, especially in their legs.
This happens mainly due to dehydration and loss of minerals. Cramps are a sign of an electrolyte disbalance.
The best strategy to treat muscle cramps is to increase the amount of electrolytes you’re having and to properly track them.
The 3 electrolytes you need to keep an eye on are sodium, potassium, and magnesium.
Potassium should come from the food you’re eating, while sodium and magnesium can be supplemented.
For more information on electrolytes, check out this electrolyte guide!

#5. Decreased Physical Performance
A relatively common but short-term effect of the keto diet is decreased physical performance.
As carbohydrates are usually the main source of energy for your body, once you restrict them at once, you might experience a loss of strength and endurance while your body adapts (10).
However, once your body adapts to ketosis, it returns to its previous physical state and performance.
Moreover, studies have also shown no negative effect of ketogenic diets on strength performance, and sometimes even an increase in performance for endurance sports (11, 12).
Getting enough sodium and potassium could help with this adverse effect.
#6. Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia)
Another common side effect is low blood sugar or hypoglycemia.
Hypoglycemia is related to different types of symptoms, such as headaches, blurred vision, dizziness, irregular heart rhythm, and irritation. It could even result in seizures or unconsciousness (13).
Carbohydrates are the main source of glucose. Therefore, the restriction of carbohydrates may result in lower glucose levels.
Hypoglycemia is relatively uncommon among people without diabetes.
If you have diabetes, though, and especially if you’re taking medication to control your blood sugar levels, you should discuss your diet with your doctor and do it under medical supervision.
The keto diet can, indeed, be very beneficial for people who have type 2 diabetes, and can even be used as a successful strategy to manage the condition (14).
#7. Increased Heart Rate (Heart palpitations)
Another side-effect that some people experience is heart palpitations. Heart palpitations occur when you feel your heart beating too fast or too hard.
This is a symptom that occurs frequently in the first days of the keto diet and can be improved with sufficient electrolyte intake.
When you begin the keto diet, you experience an initial water loss, combined with a rapid loss of electrolytes. This is why it’s essential to replenish them, together with staying well-hydrated.
You could simply add more salt to the food you eat, or to the water you’re drinking throughout the day.
Other Less Common Issues on A Low Carb Diet
Insomnia
Some people experience difficulty with either falling or staying asleep in the first weeks after they start a low-carb diet. This is usually a temporary thing.
Check out our article on how to deal with insomnia on keto to learn more about why this happens and the solutions you could try.
Reduced Bone Mineral Content (BMC)
Studies showed that children with epilepsy on a keto diet may report bone mineral content loss (15, 16).
However, these studies face many limitations and in most cases, the reduced bone mineral content was caused by a vitamin deficiency.
Kidney Stones Formation (Nephrolithiasis)
Formation of kidney stones is also a less common side effect associated with the keto diet. The majority of people who developed kidney stones had increased risks of nephrolithiasis (17, 18).
To minimize the risk, you should be getting enough potassium from your diet (which is particularly important on keto), drinking lemon water, or supplementing with apple cider vinegar (19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25).
Temporary Hair Loss
Some people say they experience some hair loss in the first weeks of keto. This is NOT a very common adverse effect and is always temporary.
In fact, many people experience better and healthier hair and nail growth on keto.
If you still experience hair loss on keto, it’s likely due to many factors and probably not from the keto diet itself, but likely because of the caloric deficit that you need to stay in, in order to achieve weight loss.
It could mean you are not eating enough calories, protein, or essential micronutrients that your body needs to grow hair, nail, and skin.
Collagen (or gelatin) and biotin could potentially help.
You can get collagen from your diet, especially from bone broth, or eating meat skin, or supplements.
One of the best ways to get enough of it in your diet is supplementing with collagen protein powder.
You can easily add it to your coffee, smoothie, drinks, and food. Many people notice a huge difference in their hair and nails growth after taking collagen for a few weeks.
Keto Rash
Although quite uncommon, a keto rash or itching is a possible side-effect of this diet.
As your body enters ketosis, it produces the ketone acetone, which can be irritating in high concentrations.
Comfortable clothing, frequent showers and avoiding exercises or places that will make you sweat can help.
In contrast to this, the keto diet has been shown to have many therapeutic uses, including improved skin quality and reduced acne (26).
Raised Cholesterol Levels
Many studies have shown that the keto diet improves cholesterol levels (27, 28, 29).
However, a few people might experience a temporary rise in cholesterol levels on a low carb diet during the first 6 months. After that, LDL-cholesterol levels will usually decrease (30).
As the mechanism by which this happens is not clear, omega-3 fatty acid supplements can be used as a preventive method against raising cholesterol levels (31).
Related: Can Weight Loss and Keto Cause Your Cholesterol Levels Go Up?
Reduced Tolerance to Alcohol
As your liver is burning fat and producing ketones, it has less capacity to burn alcohol, hence your tolerance to alcohol is decreased.
Therefore, you should be careful of the number of drinks you consume. Usually, you’ll need half the amount, compared to before, to feel the same effects.
If you want to know which low carb alcohol you can drink, check this list!
Selenium Deficiency
A rather rare reported complication of the ketogenic diet is the selenium-deficiency and its related cardiomyopathy (32, 33).
This side-effect is very rare and it can easily be prevented by adding selenium supplements to your diet, or eating foods rich in selenium, such as Brazil nuts, fish, mussels, ham, and more (34).
Acute Pancreatitis
Another rare side effect of the ketogenic diet is acute pancreatitis (35, 36).
Although acute pancreatitis is a serious condition, its incidence in people who follow a ketogenic diet is extremely low and there is no clear scientific association between ketogenic diet and pancreatitis (37).
It would be advisable for people with high triglyceride levels and other issues related to lipid metabolism to consult with a doctor prior to starting a ketogenic diet.
Gastrointestinal (GI) Intolerance
Typically, the ketogenic diet is rather high in fat compared to other diets, especially if you were following a low-fat diet before.
This could cause fat intolerance or a general gastrointestinal intolerance or discomfort. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and cramping (38).
The study that documented this side effect, however, demonstrates that the majority of the GI symptoms were related to antiepileptic drugs and steroid medication that patients had received prior to starting a ketogenic diet (39).
In fact, many people who start the ketogenic diet experience better gastrointestinal control compared to a standard American diet, especially if you were experiencing symptoms before.
This is because the keto diet eliminates most inflammatory foods that are common triggers for Gi distress, such as gluten, soy, refined sugars, and grains.
If you’re still experiencing GI problems after starting keto, then consider reducing your dairy intake and be sure you’re getting enough fiber from low-carb veggies.
How To Prevent and Treat the Possible Side Effects of a Ketogenic Diet
Although there are some side effects, which can seem unrelated to each other, they occur mostly because your body is adapting to being in ketosis.
There are some simple methods to prevent or treat the adverse effects of the keto diet:
- Give your body enough time to adjust.
Most side effects, including the keto flu, bad breath, and diarrhea happen because your body needs time to adapt to being in ketosis.
- Drink plenty of water.
Dehydration is quite common among people who begin a ketogenic diet and can also be related to other side effects.
Nevertheless, you don’t need to drink enormous amounts of water either – usually just being mindful of how much you’re drinking is sufficient.
- Increase your intake of electrolytes: sodium, potassium, and magnesium.
A rapid loss of electrolytes usually occurs when you first restrict carbs, because of the water weight you lose at first.
In general, the ketogenic diet is diuretic, meaning that water and electrolytes are flushed from your system at a higher than usual rate. This can cause heart palpitations, fatigue, leg cramps and a decrease in physical performance.
To resolve this, you need to supplement with sodium (found in table salt) and magnesium and make sure you’re getting enough potassium from your food.
- Add fiber to your diet.
Digestive problems, and especially constipation, usually occur due to a lack of sufficient fiber in your diet. Make sure you’re eating enough low-carb vegetables that are rich in fiber.
Are There Any Long-Term Side Effects from Keto?
Currently, there aren’t many studies that have examined the long-term effects of the diet, if you, for example, stay keto for more than 6-12 months at a time (or more).
One study on obese patients following a ketogenic diet for 24 months, after analyzing cholesterol, triglycerides, and blood glucose levels, concluded that the diet is safe for similar periods of time (40).
Doing keto for a few years or for life, though? There is very little information available.
If you’re following a properly formulated ketogenic diet, meaning you are getting adequate protein, fiber, and micronutrients, and keeping track of your electrolytes), it’s most likely to be safe – even in the long run.
Many people feel best on keto and report staying on it for years without experiencing any negative effects.
Nevertheless, if you decide to stay keto for long periods of time, we encourage you to do routine health checks every 6 to 12 months (including blood work) and to discuss it with your doctor.
If you’re not smart about your diet, there are potential negative outcomes from doing keto long term. This has to do with the way you handle dieting rather than with keto in particular.
- Loss of muscle mass
If you’re not consuming adequate protein, your lean body mass might decrease with time. This is not an issue if your protein is sufficient, though.
- Potential nutritional deficiencies
If you’re not eating enough veggies to get all of your essential vitamins and minerals from them, you might slowly develop micronutrient deficiencies.
Check this list of best low-carb vegetables if you need some ideas.
- Psychological side effects of long-term dieting
If you’re prone to disordered eating, counting macros and completely restricting foods might not be the best strategy for you.
Keto might feel too restrictive, as well, and you might accumulate diet fatigue and have episodes of guilt feelings if you eat non-keto foods.
If you recognize yourself in any of this, keto might not be a good long-term solution for you.
Does Keto Diet Shorten Lifespan?
We already debunked the myth that a low carb diet might link to increased mortality. You can read our full review here!
Is Keto Bad and Dangerous or Healthy?
Keto diet is generally healthy for most people. There are so many scientific studies that support this way of eating.
You can check this long list of studies here!
Here’s the thing: You don’t need to stay keto for life.
If you adapt sensible, healthy eating habits and get enough movement in your daily life, you won’t gain the weight back.
If, however, you enjoy keto and feel good on it, if your blood work doesn’t show any worrying effects, and if your doctor is okay with your choice, there is no reason not to stay keto for longer periods, too.
Conclusion
The keto diet is a proven treatment for drug-resistant epilepsy and also a powerful tool to fight obesity and manage diabetes.
Many people have transformed their lives as a result of following this diet. You can read their success stories here.
Nonetheless, as with every diet, it also has some side effects. The most common ones being keto flu, bad breath, stomach issues, hypoglycemia, dehydration, or an electrolyte disbalance, all of which can easily be prevented or treated with dietary supplements, medication or simply by giving your body enough time to adjust.
Some more serious complications involve bone mineral content loss, nephrolithiasis, and acute pancreatitis, which, however, are extremely rare and are often associated with previous medical conditions.
If you have any chronic or serious health problems, please consult a doctor prior to starting a ketogenic diet, and especially if you’re taking medication for those.
The benefits of a ketogenic diet far outweigh the side effects, which are usually minor and temporary. Give keto an honest try to experience the full benefits of being in ketosis, and of taking control of your health.
To learn more, check this Keto FAQs, Menu and Foods List.
If you find this article useful, feel free to share it with your friends!







