Because the two terms look and sound similar, many people often confuse ketoacidosis with ketosis. These conditions have very different meanings and effects on the body. One is a highly dangerous condition while the other has been shown to help you lose weight, prevent disease, and improve cognitive function.
Here’s what you need to know about the difference between ketoacidosis and ketosis.
What is Ketoacidosis?

Ketoacidosis or diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a life-threatening condition that results as a complication of type one diabetes. It occurs when there are dangerously high blood ketone levels and blood sugar present at the same time.
Ketones are compounds that are produced when the body uses fat instead of sugar as fuel. The combination of having too many ketones and too much glucose present in your blood makes it become highly acidic. This can result in damage to the normal functioning of your kidney and liver.
Ketoacidosis can develop in the body within 24 hours and requires immediate care. The condition commonly affects people with type one diabetes who do not produce enough or any insulin. People with type two diabetes can also develop the condition.
Ketoacidosis can be triggered by improper diet, infection or illness, and not taking proper doses of insulin (in diabetic patients). Symptoms of ketoacidosis include nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Other symptoms may include a fruity odor on the person’s breath. A person’s breathing may also become rapid and shallow (1).
Ketoacidosis is the leading cause of death in people with diabetes under the age of 24. Approximately 36 percent of the people who develop ketoacidosis are under the age of 30 while 27 percent are between 30 and 50, 23 percent are between 51 and 70, and 14 percent are over 70. Studies show that approximately 2 to 5 percent of people with ketoacidosis will die as a result of the condition (2, 3).
Risk Factors For Ketoacidosis
The primary risk factor for developing ketoacidosis is type one diabetes. According to one study on people with ketoacidosis, approximately 47 percent had type one diabetes, 26 percent had type two diabetes, and 27 percent had just been diagnosed with diabetes (4).
It’s important to properly monitor your blood sugar levels throughout the day If you have diabetes or blood sugar control problems to avoid ketoacidosis. Eating a diet low in refined carbohydrates and sugars may also help prevent the condition. Additional risk factors for ketoacidosis include skipping meals or not eating enough and using drugs and alcohol excessively.
What is Ketosis?
Ketosis is a metabolic state in which your body uses ketone bodies in the blood as fuel, in contrast to a glycolysis state where it uses blood glucose as energy.
Is Ketosis Dangerous?
While ketoacidosis is very harmful and can cause organ damage, ketosis is not a dangerous condition. In fact, a keto diet has been shown to help you lose weight, prevent disease, and improve brain function (5).
Ketosis refers to the presence of ketones in the blood. Because a person in ketosis does not experience high glucose levels at the same time as they do with ketoacidosis, the condition is not dangerous. The worst thing that may happen is you develop a keto breath smell.
People who are on a low carbohydrate diet often go into a state of ketosis, but the amount of ketones in the blood are not high enough to cause acidosis. The presence of ketones in the blood is a sign that your body is burning fat as fuel instead of carbohydrates.
On a low-carbohydrate diet, you have a lower amount of glucose in the blood, which makes it easier for your body to use fat instead of sugar as fuel. This means that fat in the body will be immediately utilized as fuel and it won’t be stored as fat.
Some people might choose to use exogenous ketones supplementation to help their bodies enter ketosis faster.
Dietary Ketosis Versus Dietary Ketoacidosis
People with diabetes know that ketone bodies in their urine are a sign of a dangerous condition. It also means that their diabetes is being poorly controlled. In people with severely uncontrolled diabetes, the presence of ketone bodies in massive amounts is associated with a life-threatening state of ketoacidosis.
However, when a person purposely eats a low carbohydrate diet and has a controlled and regulated production of ketone bodies, it’s completely harmless. During nutritional ketosis, a person’s blood pH levels remain within the normal limits (6).
Here’s a good graphic comparison between ketosis and ketoacidosis:
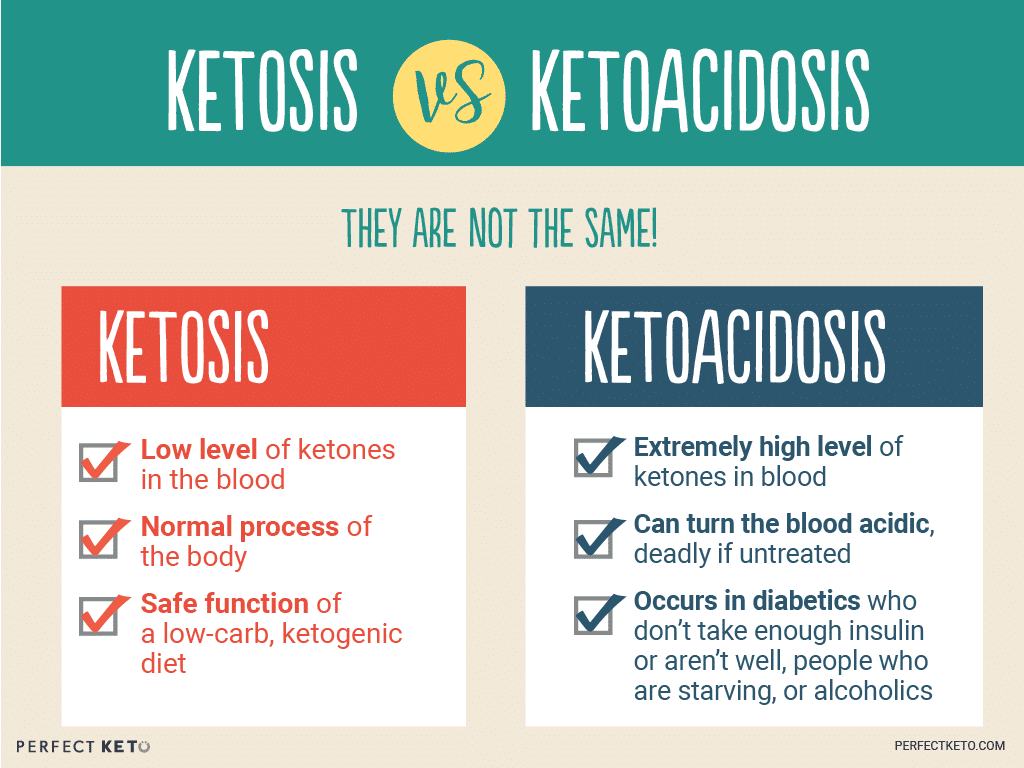
– photo courtesy of Perfect Keto –
In this state, ketones have an inhibitory effect on fatty tissue. Research shows that a mild state of ketosis has the following health benefits:
- Prevention or treatment of diseases due to insulin resistance or insufficiency
- Prevention or treatment of diseases due to free radical damage
- Prevention or treatment of diseases from hypoxia, or when the tissues become oxygen deficient
There is also evidence to suggest that insulin is not needed to turn glucose into energy in humans (6).
According to one study, there is a sufficient amount of glucose transporters in all cell membranes at all times to make sure enough glucose is taken in to satisfy the cell’s respiration requirements even if there is no insulin present at all. This means that your body’s cells are not nor have they ever been truly dependent on insulin to provide energy, which makes a high fat diet resulting in ketosis a perfectly acceptable way to fuel your body and fight disease (7).
Health Benefits of a Keto Diet
The ketogenic (keto) diet is a low-carbohydrate and high fat diet that has been shown to help you lose weight, burn fat and make you feel less hungry. However, you should remember that weight loss isn’t a linear process. The keto diet has also been shown to help you maintain muscle.
While on the ketogenic diet, ketosis kicks in after three or four days of eating less than 20 grams of carbohydrates a day. You can begin the keto process by starting with a fast and then moving into a ketogenic diet.
Research shows that children with epilepsy may benefit from a ketogenic diet by reducing the amount of seizures they have. The keto diet has also been shown to help with the following conditions:
- Epilepsy
- Heart disease
- Insulin resistance
- Type two diabetes
- Metabolic syndrome
- Acne
- Cancer (8)
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases
- Lou Gehrig’s disease
Ketosis and ketoacidosis are not the same thing. You can read our Ketogenic Diet Guide for Beginners and check our Weekly Keto Meal Plan to learn more about keto diet and get all the benefits of ketosis including weight loss.