By now, you’ve probably heard that the ketogenic diet does wonders for your body. If not, lets recap. It’s one of the best diets out there at promoting weight loss (1).
Other benefits include better blood sugar control, improved brain and heart health, and more energy throughout the day. But many people don’t know how the diet works.
The ketogenic diet is more of a lifestyle change than it is a diet, and it’s fueled by ketone bodies.
This article covers what ketones are, the three different types, how the body makes them, and how they benefit the body better than glucose.
What Are Ketones?
The ketogenic diet is characterized by a metabolic state called ketosis, which occurs when you switch your fuel source from glucose (carbs) to fat (ketones).
By definition, ketone bodies are byproducts that the body makes when there is not enough glucose in the blood and it is forced to break down fat as fuel instead.
Research shows that despite the term “bodies”, ketones are actually soluble compounds and not particles (2).
You can also think of ketones as signaling metabolites because they have been shown to control gene transcription and inhibit histone deacetylases (3).
They are also credited as being a mobile source of energy and may help link the body to environmental cues such as diet when it comes to aging (4).
In other words, if you eat a healthy diet low in refined sugar and carbs, then ketones could help slow down the aging process. But if you eat processed junk, it could make you age faster.
Unlike glucose, which is stored in the body as fat when you eat too much of it, ketone bodies build up in the blood and then spill over into the urine when there is too many of them. Then, they are excreted. This is one of the many benefits of using them as fuel in place of carbs.
Ketone bodies are produced in the liver and are always present in the blood, even if you’re not in ketosis (5).
Your levels of ketones increase as you enter the nutritional state of ketosis and your body begins to make the switch from being a glucose-burner to being a fat-burner.
Ketosis should not be confused with ketoacidosis, which is a life-threatening condition that occurs in diabetics. We’ll talk about more later in the article.
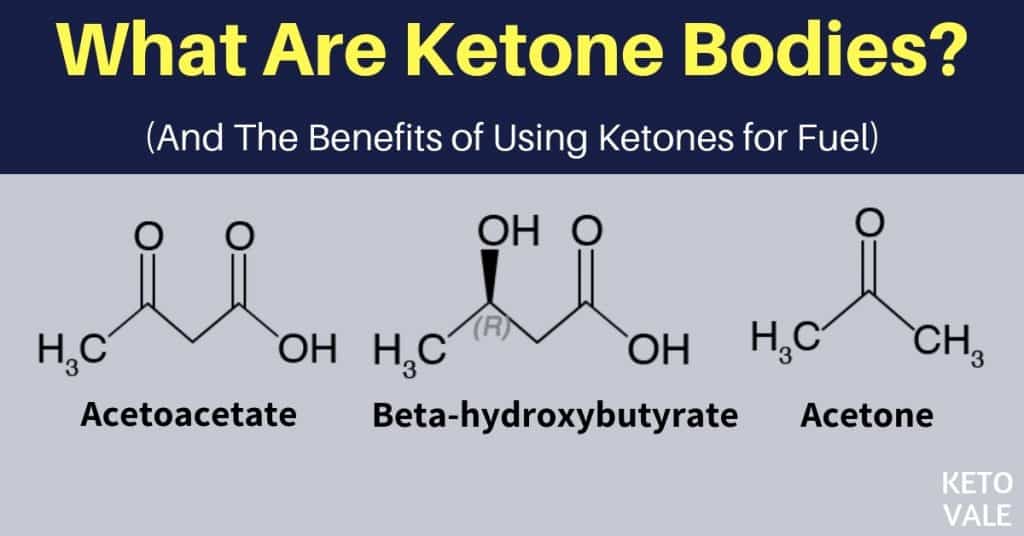
3 Type of Ketones
There are three primary types of ketones, which are listed below (6):
#1. Acetoacetate (AcAc)
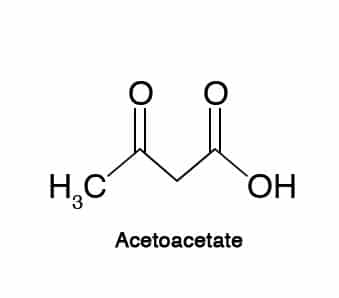
It’s produced and then utilized during the normal process of metabolism. The other types of ketones are formed through acetoacetate (7).
Research shows that acetoacetate is a more efficient energy-yielding compound than glucose. It also generates fewer species of reactive oxygen, which contributes to free radical accumulation and inflammation in the body (8).
In fact, acetoacetate oxidation ROS production 45 times better than glucose. This means that not only is it better at providing your body with energy, but it’s also less inflammatory and harmful for your body than glucose.
#2. 3-beta-hydroxybutyrate (3HB)
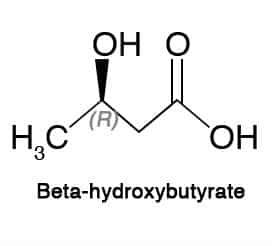
Technically speaking, 3BH is not actually a ketone body because it is reduced to a hydroxyl group during the ketonic process; however, 3BH is grouped as one of the three ketone bodies.
Research shows that it is relatively stable and transports to the tissues where it is converted into acetoacetate (10).
One study found that 3BH has important cell signaling roles in the body that may help prevent type 2 diabetes (11).
Specifically, 3BH inhibits histone deacetylases from binding to at least two surface receptors. It also contributes to the NAD+/NADH ratio, which helps regulate enzymes that are involved in the aging process (12).
#3. Acetone
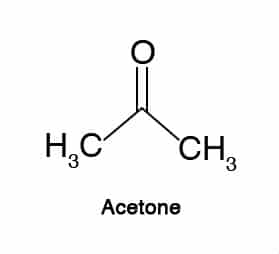
As a metabolite of acetoacetate, acetone has been shown to protect against seizures (13).
Research shows that the majority of acetone is excreted through urine and is lost during expiration (14).
How Does The Human Body Produce Ketones?
As we mentioned above, ketones are produced within the liver cells. When you start eating a low carb high fat diet and limiting your daily carb intake to around 20 – 25g for most people, your body will start producing ketones.
The primary reactions involved in ketone production include lipolysis and acyl-CoA transport across the mitochondrial membrane.
lIpolysis is a term used to describe the breaking down of fats through hydrolysis to release fatty acids. Acyl-CoA is a group of enzymes that are needed to transport the fatty acids across the cell membrane.
Research shows that the overall steps involved in the process of ketones include the breaking down of fatty acids through the process of lipolysis from fatty tissue, plasma fatty acid transport, followed by fatty acid activation, and finally fatty acid transport into the cells along with oxidation (15).
The process of synthesizing ketone bodies involves the following three steps:
- The formation of acetoacetyl-CoA
- The formation of acetoacetate
- The reduction or breakdown of acetoacetate to 3BH
In other words, when you stop eating carbohydrates, your body begins to look for another source of fuel to use for energy. Fat is the next best choice.
When you first eliminate your carbohydrate intake, your body uses up all the stored glycogen it has until it’s forced to switch over to fat. This can take up to two weeks, depending on what your storage levels are like.
When you eat a high-fat diet and restrict carbs, your body sends those fatty acids to your liver where the above-mentioned process begins and it breaks down fatty acids into ketones that are released into the bloodstream and used as energy.
You can follow this low carb food list and meal plan to start making your body use fat for fuel.
Benefits of Using Ketones for Fuel
In addition to being the more efficient source of energy for your body, ketones provide a bunch of health benefits that most people aren’t aware of. We’ll list them below.
#1. Quick and Stable Source of Energy
Unlike glucose, which must go through the entire digestive system to be processed, ketones are sent right to the liver where they are processed quickly (16).
This means that ketones can be used as fuel quicker and more efficiently than glucose can. So when you eat a high-fat meal, you won’t have to wait hours for your body to break it down. You’ll have energy within minutes.
Once your body is fat adapted, the ketones produced from dietary fats and your own body fat can fuel you and keep you going for hours (or even days for those who fast) without the need to eat. That’s why many people find intermittent fasting is easier to do when the fat adaptation process kicks in.
#2. Leaner Source of Energy
Ketones are not stored as fat in the body like glucose is. This means that even if you have too many ketone bodies present in your blood, your body will simply excrete them via your urine instead of sending them to your fatty tissues where they accumulate and contribute to your waistline. This entire process helps keep you lean.
This also applies for exogenous ketones. When you consume exogenous ketones, such as these Perfect Keto Base products, your body will use it for energy and excrete the rest as urine if you take too much of it.
#3. Better for Your Brain
In addition to being metabolized quickly in the liver, ketones can cross over the blood-brain barrier where they can be used as a quick source of fuel for your brain (17).
Additionally, ketones are a carbon source for glutamate, which can help balance the glutamate and glutamine levels in the brain. This is important because this ratio is responsible for energy metabolism and recovery during an ischemic event.
Ketones also increase the number of mitochondria your brain cells have, which can help with cognitive processes (18).
Research shows that ketones may even help protect against Alzheimer’s disease and dementia (19).
#4. Lowers Your Blood Sugar Levels and Aids in Weight Control
One of the most obvious health benefits to using ketones as fuel is that it improves your glycemic response. Since you aren’t eating carbohydrates anymore, your body doesn’t need as much insulin.
There is no blood sugar to sit in your bloodstream and cause spikes. Additionally, the limited intake of glucose means that excess amounts won’t be stored as fat, so your waistline will thank you as well.
#5. Reduces Inflammation
Sugar (glucose) is inflammatory (20).
So when you eliminate it from your diet, you are automatically cutting down on inflammation. Additionally, research shows that ketone production cuts down on ROS species in the body, which further contributes to the anti-inflammatory effect that ketones have (21).
Some research even shows that ketones have antioxidant abilities in the body, which helps eliminate free radicals that contribute to chronic inflammation and disease (22).
#6. Improves Heart Health
According to an interesting study conducted in 2016, a failing heart may rely on ketones to help it get better. The study indicated that when your heart fails, it becomes starved for energy and begins to utilize fatty acids to help keep it going (23).
Ketosis vs Ketoacidosis
Although the two words look similar, there is a big difference between ketosis and ketoacidosis.
Most people on the ketogenic diet enter ketosis willingly, and it’s often referred to as nutritional ketosis to medical experts.
Nutritional ketosis occurs when you purposely starve the body of carbohydrates and feed it a high-fat diet to prompt the body to burn fats as fuel.
As a result, the body breaks down fatty acids and ketones are produced as a byproduct. It’s a perfectly healthy and acceptable metabolic state to be in, and as we’ve mentioned above, it contains a wide variety of health benefits.
On the other hand, ketoacidosis is a life-threatening condition that occurs in people with diabetes (24).
During ketoacidosis, people with type 1 diabetes (the autoimmune kind) suffer from a dangerous build up of ketones in their blood, which is toxic in extremely high amounts. This makes your blood too acidic and and your liver and kidneys suffer as a result.
If you don’t have type 1 diabetes, then you don’t have to worry too much about ketoacidosis. It occurs when a person with this condition misses one or two of their insulin doses. It can also occur as a result of an infection or another illness.
The bottom line is that most healthy people on the ketogenic diet won’t accumulate the large amount of ketones in their blood that results in ketoacidosis. This is why the ketogenic diet is something you’ll want to talk to your doctor about before starting if you have type 1 diabetes.
How to Measure Your Ketone Levels
You can test your ketone levels in your blood and breath (using ketone meters) or in your urine (using ketone test strips).
To learn more, check our ketone testing guide here!
Conclusion
Ketone bodies are the driving force behind the ketogenic diet, but most people don’t know what they are or how they’re produced. This article discussed the three main types of ketone bodies and their important role in the body.
The biggest benefit to using ketones and not glucose as fuel is that they are a better, more efficient source of fuel. They are also metabolized quicker so that you can get the energy you need from your food immediately.
Research shows that ketones are good for your brain and may help boost cognitive performance as they can cross the blood-brain barrier. They have also been shown to help your heart out in times of failure and may even have antioxidant roles in the body. If you haven’t already, we recommend trying the ketogenic diet to see what ketones can do for you.
Up Next: The Ultimate Guide to MCT Oil